What Is Cybersecurity
Imagine waking up one day to find your bank account drained, your social media accounts hacked, and your private information exposed. Sounds like a nightmare, right? This is where cybersecurity comes in.
So why Is cybersecurity important? Cybersecurity is the practice of protecting computers, networks, and data from unauthorized access, theft, and damage.
In today’s digital world, where we rely on the internet for everything—from shopping to banking—keeping our online information safe is more important than ever.
Without strong network security, application security, and information security, personal and financial data could easily fall into the wrong hands.
Hackers and cybercriminals are always on the lookout for vulnerabilities, targeting both individuals and organizations.
Data breaches, identity theft, and ransomware attacks are just a few threats lurking in the digital shadows. This is why companies invest in cybersecurity professionals, ensuring their systems remain protected.
Break into this high-paying industry with confidence—jumpstart your cybersecurity career with quality study materials from Prepsaret.
Types of Cybersecurity
Cybersecurity isn’t just about installing an antivirus program—it’s a broad field with multiple layers of protection. Here are the key types:
- Network Security: Protects internet connections and prevents unauthorized access.
- Application Security: Ensures software and apps are secure from cyber threats.
- Information Security: Protects sensitive data from breaches and leaks.
- Operational Security: Focuses on policies and procedures to safeguard systems and data.
- Disaster Recovery and Business Continuity: Plans for quick recovery after a cyberattack or system failure.
- End-User Education: Educating individuals on safe online practices to prevent attacks.
Each of these components plays a vital role in creating a strong defense against cyberattacks.
Related blog post: What is CompTIA Security+?
What Is a Cybersecurity Job?
With cyber threats growing daily, cybersecurity professionals are in high demand. A cybersecurity job involves protecting an organization’s data, detecting security threats, and preventing cyberattacks. Professionals in this field may specialize in roles such as:
- Security Analyst – Monitors and defends systems against cyber threats.
- Penetration Tester – Simulates attacks to find system vulnerabilities.
- Cybersecurity Engineer – Designs and implements security measures.
Continue reading: Cybersecurity Jobs
Cybersecurity Salary: How Much Can You Earn?
Cybersecurity is a lucrative field due to its high demand. Salaries vary based on experience, location, and job role.
- What is the median salary of a cybersecurity engineer? The median salary of a cybersecurity engineer in the U.S. is around $115,000–$130,000 per year, depending on experience and location.
- Entry-level cybersecurity professionals can expect to earn around $65,000–$85,000 annually.
- Senior cybersecurity professionals and specialists can make well over $150,000 per year, especially in Big Tech companies.
What Is Big Tech’s Role in Cybersecurity?
Major tech companies like Google, Microsoft, and Amazon play a crucial role in advancing cybersecurity. Big Tech invests billions in developing security solutions, including:
- Cloud Security services to protect data stored online.
- AI-powered threat detection to identify and prevent cyberattacks.
- End-user education programs to teach people about cybersecurity best practices.
Additionally, these companies actively follow and contribute to global cybersecurity frameworks.
What Is the NIST Cybersecurity Framework?
One of the most widely used security frameworks is the NIST Cybersecurity Framework, developed by the National Institute of Standards and Technology.
This framework provides guidelines for businesses to manage cybersecurity risks and improve their security posture. It is based on five key functions:
- Identify – Understanding and managing cybersecurity risks.
- Protect – Implementing safeguards to secure systems and data.
- Detect – Monitoring for security breaches.
- Respond – Taking action in response to cyber threats.
- Recover – Restoring systems and reducing damage after an attack.
Many organizations, including Big Tech companies, use the NIST Cybersecurity Framework to guide their security strategies.
The Importance of Cybersecurity in Today’s Digital World
Cybercrime is on the rise, affecting businesses and individuals alike. In 2023 alone, cyberattacks cost companies billions of dollars and exposed millions of personal records.
Cybersecurity Helps Protect:
- Financial Transactions: Online banking and shopping require strong security measures.
- Personal Data: Identity theft is a serious concern, with hackers targeting personal details.
- Critical Infrastructure: Power grids, hospitals, and government systems need protection from cyber threats.
Real-world examples like the 2017 Equifax data breach, which exposed 147 million people’s personal data, highlight the devastating impact of cybercrime. By prioritizing cybersecurity, we can prevent such disasters and keep our digital lives secure.
Key Cybersecurity Principles and Best Practices

To stay safe online, it’s important to follow fundamental cybersecurity principles:
- Confidentiality, Integrity, and Availability (CIA Triad): Ensures data remains private, accurate, and accessible to authorized users.
- Strong Passwords and Authentication: Use complex passwords and enable Multi-Factor Authentication (MFA) whenever possible.
- Software Updates and Patch Management: Regularly update software to fix security vulnerabilities.
- Security Awareness and Education: Stay informed about potential threats and how to avoid them.
Following these best practices helps minimize risks and keeps your data safe from cybercriminals.
How to Start a Career in Cybersecurity
If you’re interested in entering this field, you can take a cybersecurity course to gain essential skills. Many universities and online platforms offer training in:
- Network security and ethical hacking
- Threat detection and incident response
- Encryption and cloud security
- Compliance and risk management
Certifications like Certified Ethical Hacker (CEH), Certified Information Systems Security Professional (CISSP), and CompTIA Security+ can also help boost your career prospects.
Understanding Network Security and Its Importance
Think of your home Wi-Fi network like a castle. Without strong walls (security measures), cybercriminals can break in and steal your digital treasures.
Effective cybersecurity strategies for organizations and businesses help prevent such breaches and ensure data protection and privacy.
What is Network Security?
Network security involves measures to protect a computer network from cyber threats. It ensures that only authorized users can access sensitive information.
The role of technology in cybersecurity plays a crucial part in maintaining secure networks, with organizations leveraging advanced cybersecurity tools and technologies to defend against cyberattacks.
Types of Cyber Security
Cybersecurity covers multiple domains to protect systems, networks, and data. Some key types of cybersecurity include:
- Network Security – Protects networks from intrusions and attacks.
- Cloud Cybersecurity Measures – Safeguards data stored in cloud environments.
- IoT Security Challenges – Addresses vulnerabilities in connected devices.
- Application Security – Ensures software and apps are free from threats.
- Operational Security – Focuses on protecting internal business operations.
Understanding these categories helps individuals and businesses implement best practices for cybersecurity and protect against cyber threats.
Learn more: CompTIA Security+ Certification
Key Network Security Measures
To strengthen network security and cyberattack prevention, organizations utilize various security measures:
- Firewalls: Block unwanted traffic.
- VPNs: Secure internet connections.
- Intrusion Detection Systems: Monitor for suspicious activity.
- Unified Threat Management Systems: Combine multiple security functions for comprehensive protection.
- Security Awareness Training: Educates employees on recognizing and avoiding cyber threats.
Common Network Security Threats
Cybercriminals use various tactics to exploit vulnerabilities. Common threats include:
- Phishing Attacks: Tricking people into giving up passwords.
- Malware: Harmful software that can steal or destroy data.
- Ransomware and Phishing Defense: Protecting against attacks that lock files and demand payment.
- Man-in-the-Middle Attacks: Hackers intercept communications to steal information.
- Zero-Day Exploits: Attacks targeting unknown software vulnerabilities.
Using advanced cybersecurity tools and technologies is essential in preventing these threats.
How to Protect Your Network
Implementing cybersecurity best practices is key to maintaining a secure network:
- Use strong passwords for Wi-Fi and devices.
- Enable firewalls and security software to block unauthorized access.
- Be cautious when connecting to public Wi-Fi to prevent data theft.
- Adopt Internet Security Solutions that provide end-to-end encryption.
- Implement Secure Software Development Practices to ensure safe application deployment.
Cybersecurity Frameworks and Compliance Standards
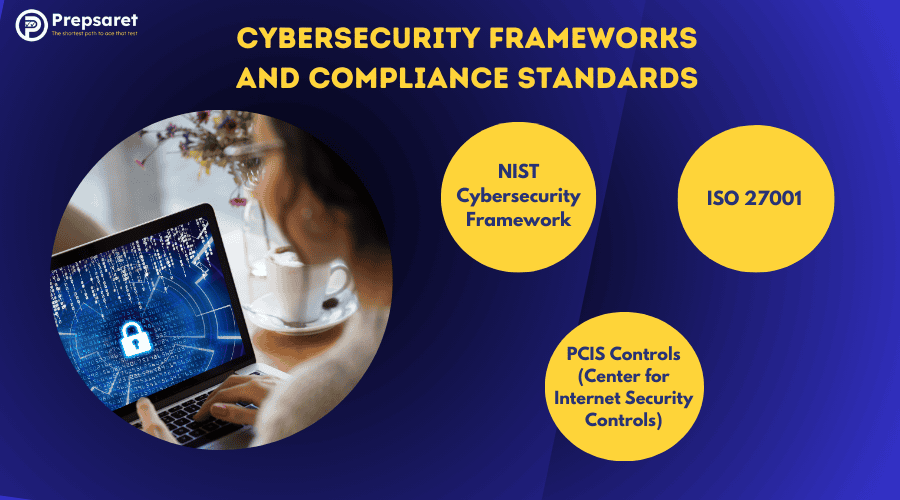
Organizations rely on well-established frameworks to protect sensitive information. Some of the most important cybersecurity frameworks include:
- NIST Cybersecurity Framework – A comprehensive set of guidelines used by businesses and governments to manage cybersecurity risks.
- ISO 27001 – An international standard for managing information security systems, ensuring that organizations follow best practices.
- CIS Controls (Center for Internet Security Controls) – A prioritized list of security measures that organizations can implement to defend against cyber threats.
Compliance Matters
Beyond frameworks, businesses must comply with laws and regulations that protect user data. Some key regulations include:
- GDPR (General Data Protection Regulation) – European privacy law that gives users control over their data.
- HIPAA (Health Insurance Portability and Accountability Act) – Protects medical information in the U.S.
- PCI-DSS (Payment Card Industry Data Security Standard) – Ensures secure handling of credit card information.
- CCPA (California Consumer Privacy Act) – Grants California residents rights over their personal data.
Ignoring these standards isn’t just risky—it can lead to hefty fines and reputational damage!
Careers in Cybersecurity: Certifications and Job Roles
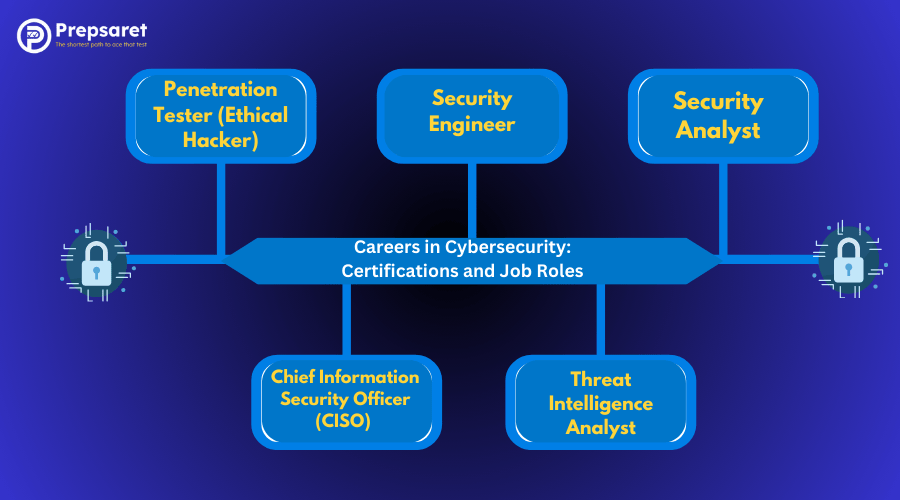
The demand for cybersecurity professionals is skyrocketing, and companies are willing to pay top dollar for skilled experts. If you’re considering a cybersecurity job, here are some exciting roles:
- Security Analyst – Monitors and defends systems against cyber threats.
- Penetration Tester (Ethical Hacker) – Simulates cyberattacks to find vulnerabilities.
- Security Engineer – Builds secure systems and develops defense mechanisms.
- Chief Information Security Officer (CISO) – Leads an organization’s cybersecurity strategy.
- Threat Intelligence Analyst – Studies cybercriminal activities to predict and prevent attacks.
Cyber Security Salary and Career Growth
Cybersecurity professionals earn competitive salaries, reflecting the high demand for their skills. Salaries vary based on experience and specialization:
- Entry-level (Security Analyst, IT Security Specialist): $60,000–$90,000 per year.
- Mid-level (Penetration Tester, Security Engineer): $90,000–$120,000 per year.
- Senior-level (CISO, Security Architect): $150,000+ per year.
Pursuing the right cybersecurity course and obtaining relevant certifications can significantly impact career opportunities.
Top Cybersecurity Certifications: CompTIA Security+ and Beyond
Certifications are a great way to break into cybersecurity jobs. Here are some of the top ones:
- CompTIA Security+ – A beginner-friendly certification that covers security fundamentals.
- CISSP (Certified Information Systems Security Professional) – Advanced certification for experienced professionals.
- CEH (Certified Ethical Hacker) – Focuses on penetration testing and hacking techniques.
- CISM (Certified Information Security Manager) – Ideal for management-level professionals overseeing security programs.
- GIAC Certifications – Specialized credentials in cybersecurity domains like incident response and malware analysis.
These certifications open doors to high-paying jobs and career growth.
Read on: Best Cybersecurity Certification
How to Get Started in Cybersecurity: A Beginner’s Guide
Ready to dive into cybersecurity? Here’s how to start:
- Learn the Basics – Understand networking, operating systems, and basic security concepts.
- Take Online Courses – Platforms like Prepsaret, Coursera, and Cybrary offer beginner-friendly cybersecurity courses.
- Read Books – Titles like The Web Application Hacker’s Handbook and Cybersecurity for Dummies provide valuable insights.
- Practice Hands-On – Use virtual labs like Hack The Box or TryHackMe to sharpen your skills.
- Get Certified – Start with CompTIA Security+ and build from there.
Steps to Build a Strong Cybersecurity Strategy
Cybersecurity isn’t a one-time fix—it’s an ongoing process. Here’s a simple strategy:
- Identify Assets and Vulnerabilities – Know what needs protection and where the risks are.
- Implement Best Practices for Cybersecurity – Use strong passwords, enable multi-factor authentication, and update software regularly.
- Use Internet Security Solutions – Adopt tools like antivirus software, intrusion detection systems, and secure cloud storage.
- Monitor and Improve Continuously – Stay updated with the latest cyber threats and adjust your security measures accordingly.
- Develop an Incident Response Plan – Ensure your organization is prepared to handle security breaches effectively.
By implementing robust cybersecurity strategies for organizations, companies can protect against cyber threats, ensuring secure and resilient operations.
Find out: How Long Does It Take to Prepare for CompTIA Security+?
Final Thoughts
Cybersecurity is more important than ever, protecting personal and business data from cybercriminals.
Whether you’re an individual looking to stay safe online or considering a cybersecurity job, understanding network security, information security, and the NIST Cybersecurity Framework is crucial.
With Big Tech leading advancements and growing demand for cybersecurity professionals, this field offers lucrative opportunities for those who choose to specialize in it.
Would you like to secure your future in this industry? Start by exploring a cybersecurity course today!
FAQs
What Is A Cybersecurity Job?
A cybersecurity job involves identifying and mitigating risks to computer systems and networks. Professionals monitor for threats, secure data, and implement protective measures like firewalls and encryption.
They specialize in areas such as ethical hacking or incident response. Their primary goal is to prevent breaches that could compromise sensitive information or disrupt operations.
Cybersecurity roles are essential across industries due to the increasing dependence on digital tools.
What Are The 5 Types Of Cybersecurity?
The five main types of cybersecurity are network security, application security, information security, cloud security, and IoT security. Network security defends networks from unauthorized access. Application security protects software from vulnerabilities.
Information security safeguards data's confidentiality and integrity. Cloud security focuses on securing cloud-based systems, while IoT security protects internet-connected devices. Each type addresses specific aspects of protecting digital environments against evolving threats.
What Is The Main Purpose Of Cybersecurity?
The main purpose of cybersecurity is to protect sensitive information, systems, and networks from cyberattacks. This includes ensuring data confidentiality, maintaining digital asset integrity, and ensuring availability to authorized users.
Effective cybersecurity prevents financial losses, protects personal privacy, and ensures the smooth functioning of businesses and critical infrastructure in a connected world. It plays a vital role in maintaining trust and security in digital environments.

