Mastering how to troubleshoot network issues for CompTIA Network+ is more than just checking a box on your Network+ certification checklist, it’s the foundation of real-world IT success.
When networks go down (and they will), employers need someone who can jump in, diagnose fast, and fix the problem without breaking a sweat. That someone could be you.
To build those hands-on skills and boost your confidence, check out Prepsaret’s Network+ self-study prep program. It’s packed with everything you need to crush the Network+ exam—clear explanations, practical examples, and all the troubleshooting know-how to turn you into a networking pro.
Why Network Troubleshooting Matters for the CompTIA Network+ Exam
CompTIA Network+ network issues are a central focus of the certification exam for a simple reason: troubleshooting is what network professionals do every day.
According to CompTIA, approximately 24% of the Network+ exam focuses on troubleshooting scenarios, making it one of the most heavily weighted domains.
The Network+ exam troubleshooting sections test your ability to identify problems, apply the right solutions, and verify results—skills that directly translate to workplace performance. Employers value these practical abilities even more than theoretical knowledge because they reduce network downtime and keep businesses running smoothly.
When you face Network+ certification troubleshooting simulation questions, you’ll need to demonstrate problem-solving skills under time pressure, just like in a real network emergency.
These performance-based questions often simulate common networking issues and ask you to identify the problem and recommend solutions.
Network Troubleshooting Steps
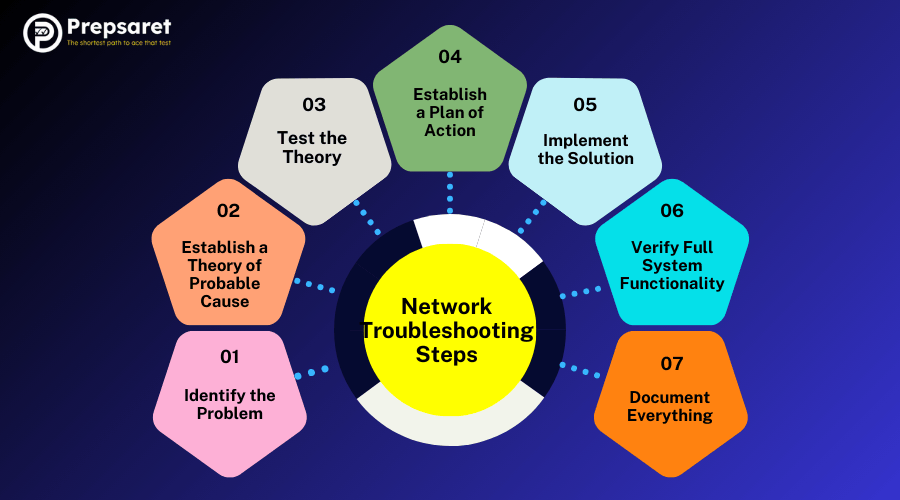
Troubleshooting network issues isn’t about guesswork—it’s about following a smart, step-by-step process. Whether you’re studying for the exam or solving real-world tech headaches, you need a clear plan.
So, what is the first step in troubleshooting a network? Let’s break it down.
Step 1. Identify the Problem
Always start here. Before diving into tools or commands, take a breath and get the full picture. Skipping this step often leads to confusion, wasted time, and the wrong fixes.
Here’s how to do it right:
- Ask the right questions
- When did the issue start?
- Who is affected—just one user or the whole network?
- Has anything changed recently—new devices, updates, or configurations?
- Can the issue be reproduced?
- Gather info like a pro
Use logs, monitoring tools, error messages, and talk to users. The more you know, the better your chances of hitting the root cause. - Replicate the problem
Try to recreate the issue in a controlled way so you can see it in action. - Document everything
Write down symptoms, patterns, and affected systems. If there are multiple problems, separate them clearly.
Once the problem is well defined, you’re ready for the next step.
Step 2: Establish a Theory of Probable Cause
Now that you’ve gathered all the clues, it’s time to play detective. What’s most likely causing the issue?
Start by developing possible explanations based on what you found in Step 1. This is where logic meets curiosity.
- Ask the obvious: Is everything plugged in?
- Think both simple and deep—don’t rule anything out too fast.
- Use the OSI model as your guide to track down where the issue might be (cables, IP addresses, apps—you name it).
Step 3: Test the Theory
Now test your ideas. Don’t just assume you’re right—prove it.
- Use network troubleshooting tools or commands to verify each theory.
- If one of your guesses is confirmed—awesome! You’re ready to fix it.
- If nothing sticks, don’t panic. Go back to your list or ask a teammate for a second opinion.
Step 4: Establish a Plan of Action
Found the cause? Great. Now let’s fix it—but with a plan.
- Think about how your fix will affect the rest of the network.
- Make sure your solution won’t break something else by mistake.
- If you can, test it in a safe environment (like a lab setup) before making changes on live systems.
Step 5: Implement the Solution
Time to put your plan into action!
- Follow your steps carefully.
- If it works—nice job!
- If it doesn’t, or it’s above your pay grade, escalate the issue to someone more experienced. (That’s teamwork, not failure.)
Step 6: Verify Full System Functionality
You applied the fix, but don’t walk away just yet.
- Make sure everything’s working across the board.
- Double-check that you didn’t create a new issue while solving the original one.
- Ask users if everything’s back to normal.
Step 7: Document Everything
This is the step most people skip—but it’s super important.
- Write down what the problem was, how you fixed it, and what the outcome was.
- Good notes save time when similar issues pop up again.
- Plus, it helps your whole team learn and improve.
Following the Network+ troubleshooting steps in order helps ensure you don’t miss important clues or jump to incorrect conclusions.
Remember that thorough information gathering at the beginning can save hours of trial and error later.
Find Out: How to Start Studying for CompTIA Network+
Tools Used in CompTIA Network+ Troubleshooting

The right network troubleshooting tools can make all the difference in quickly identifying and resolving issues. Here are essential network troubleshooting tools Network+ professionals rely on daily:
Command-Line Utilities:
- Ping – Tests connectivity between devices
- Tracert/Traceroute – Maps the path data takes through the network
- Ipconfig/Ifconfig – Displays IP configuration information
- Nslookup/Dig – Queries DNS servers for name resolution
- Netstat – Shows active network connections
Hardware Tools:
- Cable testers – Verify cable integrity
- Multimeters – Test electrical signals
- Toners and probes – Locate and identify cables
- Loopback adapters – Test network interfaces
Software Applications:
- Wireshark – Captures and analyzes network traffic
- Network analyzers – Monitor performance metrics
- Port scanners – Identify open ports and services
Understanding which tools used in CompTIA Network+ troubleshooting apply to different situations is crucial for the exam.
The Network+ certification evaluates your ability to select the right tools for different troubleshooting scenarios. To succeed, it’s important to practice using these tools in various contexts.
To ensure you’re fully prepared, rely on the best study resources for CompTIA Network+, especially those that are regularly updated. This will help you gain the knowledge and confidence needed to choose the correct tools in real-world situations.
Network Troubleshooting Commands You Must Know
Network troubleshooting commands form the foundation of your diagnostic toolkit. These commands allow you to gather information, test connectivity, and identify configuration issues from the command line.
Let’s look at how to use ping and tracert in troubleshooting:
Ping Command Examples:
C:\> ping 192.168.1.1
C:\> ping -t google.com
C:\> ping -n 10 8.8.8.8
The ping command sends ICMP echo requests to verify connectivity. No response indicates a potential network issue or firewall blocking ICMP.
Tracert/Traceroute Examples:
C:\> tracert google.com
$ traceroute 8.8.8.8
These commands show the path packets take through the network, revealing where delays or breaks in connectivity occur.
Knowing how to troubleshoot network issues for CompTIA Network+ requires mastery of these commands and interpreting their output.
For example, if ping shows high latency but tracert identifies a specific hop with delays, you’ve narrowed down the problem to a particular segment of the network path.
Other essential commands include:
- ipconfig /all (Windows) or ifconfig (Linux) – Shows detailed IP configuration
- nslookup or dig – Tests DNS resolution
- netstat – Displays active connections and listening ports
- nbtstat – Shows NetBIOS over TCP/IP information
Practice these commands until you can interpret their output quickly and accurately.
Try Out: Free CompTIA Network+ Practice Questions
Understanding the OSI Model in Troubleshooting
How does the OSI model help in network troubleshooting?
The OSI (Open Systems Interconnection) model provides a structured framework for breaking down complex network problems into manageable layers.
By understanding which layer contains the problem, you can focus your troubleshooting efforts more efficiently.
Troubleshooting OSI model Network+ expertise is essential for passing the exam. Here’s how to approach each layer:
- Physical Layer (Layer 1) – Check cables, connectors, power, and physical hardware
- Data Link Layer (Layer 2) – Verify MAC addresses, switches, and frame transmission
- Network Layer (Layer 3) – Examine IP addressing, routing, and packet forwarding
- Transport Layer (Layer 4) – Analyze TCP/UDP ports, connections, and data delivery
- Session Layer (Layer 5) – Look at session establishment and management
- Presentation Layer (Layer 6) – Check data formatting, encryption, and compression
- Application Layer (Layer 7) – Test applications, services, and user interfaces
How to Isolate Network Issues by Layer
How to isolate network issues by layer is a skill that develops with practice. Start at either the physical layer and work up, or the application layer and work down, systematically eliminating potential causes at each layer.
For example, if a user can’t access a website:
- Layer 1: Are all cables connected?
- Layer 2: Is the switch functioning properly?
- Layer 3: Can the device ping its default gateway?
- Layer 4: Is the web port (80/443) accessible?
- Layer 7: Is the web browser configured correctly?
Learning how to troubleshoot network issues for CompTIA Network+ using the OSI model makes complex problems much more manageable.
Check Out: How to Use Flashcards for CompTIA Network+ Prep
Common Network Issues You’ll Encounter
Recognizing examples of network connectivity issues will help you prepare for both the Network+ exam and real-world troubleshooting scenarios. Here are common problems you should know how to identify and resolve:
- IP Configuration Issues:
- IP address conflicts
- Incorrect subnet mask
- Default gateway misconfiguration
- DHCP server problems
- DNS Problems:
- Failed name resolution
- Incorrect DNS server settings
- Stale DNS cache
- Physical Connectivity Issues:
- Damaged cables
- Faulty network interface cards
- Port configuration errors
- Power-related problems
- Performance Concerns:
- Network congestion
- Bandwidth limitations
- Duplex mismatches
- Broadcast storms
CompTIA Network+ practice troubleshooting often focuses on these common issues. When studying, create scenarios that simulate these problems and practice applying the troubleshooting methodology to solve them.
Network+ troubleshooting performance issues requires understanding baseline performance and recognizing deviations. Tools like Performance Monitor in Windows or top in Linux can help identify resource bottlenecks.
Knowing how to identify network issues Network+ is all about recognizing patterns in symptoms. For instance, if multiple devices can’t access the internet but can communicate with each other, the problem likely lies with the default gateway or beyond.
The CompTIA Network+ exam will test your ability to recognize these patterns, so it’s important to practice effectively for the test.
This will help you apply your troubleshooting skills in real-world scenarios, ensuring you’re ready to handle network issues confidently
How to Troubleshoot Network Issues in Windows 10

Troubleshooting in Windows 10 requires familiarity with several built-in tools that can help diagnose and resolve connection problems:
Windows Network Diagnostic Tools:
- Network and Sharing Center – Provides access to adapter settings, troubleshooting wizards, and connection details
- Device Manager – Helps identify hardware issues and update drivers
- Windows Event Viewer – Logs system events including network-related errors
- Windows Performance Monitor – Tracks network performance metrics
- Windows PowerShell – Offers advanced networking commands
- Command Prompt – Provides access to ipconfig, ping, tracert, and other utilities
To reset your network in Windows:
- Go to Settings > Network & Internet > Status
- Scroll down and select “Network reset”
- Click “Reset now”
This can solve many connection issues by reinstalling network adapters and resetting TCP/IP stack to default settings.
Windows firewall can also cause connectivity issues. Check if it’s blocking necessary traffic:
- Search for “Windows Defender Firewall” in the Start menu
- Select “Allow an app or feature through Windows Defender Firewall”
- Verify that your applications have the appropriate permissions
Understanding Windows-specific networking components is crucial for the Network+ exam, as Microsoft environments remain common in enterprise settings.
Find Out: Top CompTIA Network+ Books
Real-World Network Troubleshooting Scenarios
Real-world network troubleshooting scenarios prepare you for both the exam and workplace challenges. Let’s examine some common situations you might encounter:
Scenario 1: Users Can’t Access the Internet
- Symptoms: Multiple users report no internet access
- Investigation: Ping tests to local devices succeed, but external domains fail
- Diagnosis: Default gateway is unreachable
- Solution: Router needed to be rebooted after firmware update
Scenario 2: Slow Network Performance
- Symptoms: File transfers and application response times have degraded
- Investigation: Network utilization shows unusual broadcast traffic
- Diagnosis: Broadcast storm due to switch loop
- Solution: Identify and remove redundant connection or implement Spanning Tree Protocol
Network+ troubleshooting questions often present similar scenarios and ask you to identify the most likely cause or the best next troubleshooting step.
The key is applying your knowledge of how to troubleshoot network issues for CompTIA Network+ systematically rather than guessing.
Practice with scenarios like these:
- A user can connect to local resources but not internet sites
- Two departments can’t communicate with each other but can access other network resources
- VoIP calls are dropping intermittently during peak business hours
- After a power outage, some devices can’t obtain IP addresses
For each scenario, practice the full troubleshooting methodology: identify symptoms, form hypotheses, test theories, implement solutions, and verify results.
Common Problems and Solutions in Network Troubleshooting
Here’s a quick reference table of network troubleshooting problems and solutions you might encounter:
| Problem | Symptoms | Possible Causes | Solutions |
| Cannot access internet | Local network works, external sites don’t load | DNS issues, default gateway problems | Check DNS settings, verify default gateway, test alternate DNS |
| Intermittent connectivity | Connection drops randomly | Wireless interference, faulty hardware, driver issues | Update drivers, check for interference, replace hardware if needed |
| IP conflict | “IP address already in use” error | Static IP assignments overlap with DHCP | Reconfigure static IPs, check DHCP scope |
| Slow network | Long loading times, poor performance | Bandwidth saturation, duplex mismatch, outdated hardware | Check traffic patterns, verify duplex settings, upgrade equipment |
| Cannot connect to specific server | Error accessing one resource | Server down, firewall blocking, route issues | Verify server status, check firewall rules, trace route to server |
Troubleshooting IP conflicts and DNS problems represents a significant portion of a network administrator’s daily tasks. For IP conflicts:
- Use “ipconfig /all” to identify the conflicting device
- Release and renew IP addresses with “ipconfig /release” and “ipconfig /renew”
- Configure static IPs outside the DHCP scope
- Use “arp -a” to find duplicate MAC addresses
For DNS issues:
- Test with “nslookup” or “dig” commands
- Clear DNS cache with “ipconfig /flushdns” (Windows)
- Try alternative DNS servers temporarily
- Check DNS server configurations
Understanding these common issues and their resolutions will help you excel in the Network+ troubleshooting sections.
Related article: Is CompTIA Network+ Worth it for Beginners?
Final Tips + Downloadable Resource
To succeed in how to troubleshoot network issues for CompTIA Network+, remember these key principles:
- Be methodical – Follow the troubleshooting steps in order
- Document everything – Keep records of what you’ve tried
- Check the simple things first – Often the problem is something basic
- Use the OSI model – Systematically work through the layers
- Know your tools – Be familiar with all troubleshooting utilities
- Think critically – Don’t jump to conclusions without evidence
For a comprehensive study aid, download the network troubleshooting PDF that summarizes all these concepts in a printable format. This resource includes common commands, troubleshooting flowcharts, and quick reference tables for exam preparation.
FAQS
What Are The 7 Steps Of Network Troubleshooting?
The seven steps are:
- Identify the problem
- Develop a theory of probable cause
- Test the theory
- Establish a plan of action
- Implement the solution
- Verify full system functionality
- Document findings and outcomes.
What Are The 7 Troubleshooting Steps From CompTIA?
CompTIA’s seven troubleshooting steps are:
- Identify the problem
- Establish a theory of probable cause
- Test the theory
- Establish a plan of action
- Implement the solution
- Verify system functionality
- Document the process and results.
What Can Be Used To Troubleshoot Network Issues Including Traffic Going Into And Out Of Instances?
Network diagnostic tools like Wireshark, network analyzers, and built-in utilities (ping, tracert, netstat) can monitor and analyze traffic going into and out of network instances. These tools help identify bottlenecks, dropped packets, and misconfigurations.
How Do You Troubleshoot An Unstable Network?
Check for loose or damaged cables, wireless interference, or faulty hardware. Update drivers and firmware, verify correct IP and DNS settings, and use diagnostic tools to monitor traffic. Restart network devices and isolate whether the issue is device-specific or network-wide.
What Is The First Step When Troubleshooting Any Network Connectivity Issue?
The first step is to identify and define the problem. This includes gathering information, checking physical connections, and confirming the scope and symptoms before moving to more advanced troubleshooting.
Looking for more practice? Check out the Prepsaret Network+ prep course which offers simulation labs that let you practice how to troubleshoot network issues for CompTIA Network+ in a safe environment before taking the actual exam.

